符号表
| 符号 | 中文 | English | 例子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| $A ∼ B$ | A1 服从 B 分布 | A is subject to distribution B | $W ∼ Binomial(N, p)$ |
| $Pr(E_A)$ | 事件 $E_A$ 的概率分布 | probability of $E_A$ | |
| $Pr(E_A, E_B)$2 | 事件 $E_A$ 和 $E_B$ 的联合概率分布($E_A$ 且 $E_B$ 的概率分布) | joint probability distribution of $E_A$ and $E_B$ | |
| $Pr(E_A|E_B)$2 | 确定事件 $E_B$ 发生时 $E_A$ 发生的概率 | “the conditional probability of $E_A$ given $E_B$” or “the probability of $E_A$ under the condition $E_B$” | |
| $E_A \mathrel{\rlap{\perp}\mkern1mu\perp} E_B$3 | $E_A$ 和 $E_B$ 无关 | $E_A$ is independent of $E_B$ | |
| $E_A {\llap{\not}}{\mathrel{\rlap{\perp}\mkern1mu\perp}} E_B$ | $E_A$ 和 $E_B$ 有关 | $E_A$ is not independent of $E_B$ |
名词解释
先验概率/Prior (probability)
在贝叶斯统计中,某一不确定量p的先验概率(Prior probability)分布是在考虑「观测数据」前,能表达p不确定性的概率分布。
A prior probability distribution of an uncertain quantity, often simply called the prior, is its assumed probability distribution before some evidence is taken into account. —— Wikipedia
简单来说就是在考虑观测数据前,对不确定量的概率分布的一个猜测。
似然函数/Likelihood function
似然函数(英語:likelihood function)是一种关于统计模型中的参数的函数,表示模型参数中的似然性(英語:likelihood)
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) is the joint probability (or probability density) of observed data viewed as a function of the parameters of a statistical model.
简单来说就是要求不确定量服从的概率分布函数。
后验概率/Posterior (probability)
在贝叶斯统计中,一个随机事件或者一个不确定事件的后验概率(Posterior probability)是在考虑和给出相关证据或数据后所得到的条件概率。
The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that results from updating the prior probability with information summarized by the likelihood via an application of Bayes' rule.
简单来说就是在考虑观测数据后,不确定量的概率分布。
Berkson’s paradox / selection-distortion effect
(Berkson’s paradox) is a result in conditional probability and statistics which is often found to be counterintuitive, and hence a veridical paradox.
是指人们的直觉观察与实际上真实的条件概率和严谨的统计结果不相符,也就是说人们所发现的看似两个相关的因素实际上根本无关。
多重共线性/Multicollinearity
Multicollinearity means very strong correlation between two or more predictor variables.
In statistics, multicollinearity (also collinearity) is a phenomenon in which one predictor variable in a multiple regression model can be perfectly predicted from the others.
多重共线性(Multicollinearity)是指多变量线性回归中,变量之间由于存在高度相关关系而使回归估计不准确。在该情况下,多元回归的系数可能会因为模型或数据的微小变化发生剧烈改变。
Will produce false inferences about causal effects.
Kullback-Leible 散度
The additional uncertainty induced by using probabilities from one distribution to describe another distribution.
即一个概率分布相对于另一个概率分布的差异程度。
We can quantify distance to the target using Kullback-Leibler divergence.
log-pointwise-predictive-density
the log of the average probability for each observation i, where the average is taken over the posterior distribution
最大熵分布
a maximum entropy probability distribution has entropy that is at least as great as that of all other members of a specified class of probability distributions
divergent transitions
when the posterior distribution is very steep in some region of parameter space. Steep changes in probability are hard for a discrete physics simulation to follow. When that happens, the algorithm notices by comparing the energy at the start to the energy at the end.
解决方式包括修改 MCMC 的接受率(adapt_delta)、reparameterize、用更好的 prior 等。
Interactions
One variable may depend upon another. For example, plants benefit from both light and water. But in the absence of either, the other is no benefit at all.
over-dispersion
Variance of a variable is larger than what would be expected from a given statistical model.
常用分布
均匀分布 / Uniform distribution
$$ Uniform(a, b) $$
即等可能地选取 $[a, b]$ 之间的任何一个数所得到的概率分布。
伯努利分布 / Bernoulli distribution
$$ Bernoulli(p) $$
做试验得到“成功”结果的概率为 $p$,那么做一次实验结果为“成功”的概率分布。
Categorical 分布
$$ Categorical(\textbf{p}) $$
做试验得到第 i 种结果的概率为 $\textbf{p}_i$,那么做一次实验结果为第 i 种的概率分布。
二项分布 / Binomial distribution
$$ Binomial(N, p) $$
每次试验得到“成功”结果的概率为 $p$,做 $N$ 次试验,得到“成功”次数的概率分布。
$N$ 为 1 时,退化为伯努利分布。
$N$ 很大而 $p$ 很小时,逼近泊松分布。
$N$ 很大而 $p$ 接近 0.5 时近似于正态分布。
多项分布 / Multinomial distribution
$$ Multinomial(N, \textbf{p}) $$
每次试验得到第 i 种结果的概率为 $\textbf{p}_i$,做 $N$ 次试验,得到某个值的次数的概率分布。
$\beta$ 分布 / Beta distribution
$$ Beta(a, b) $$
做 $a + b$ 次实验,发现其中 a 次成功,b 次失败则实验本身的成功率 $p$ 的概率分布。4
Dirichlet 分布 / Multivariate beta distribution
$$ Dir(\textbf{a}) $$
$\beta$ 分布的多变量扩展,做 $\Sigma \textbf{a}$ 次实验,其中第 $i$ 种结果出现 $\textbf{a}_i$ 次,$Dir(\textbf{a})$ 描述了其中每个结果的出现率。
指数分布 / Exponential distribution
$$ Exp(λ) $$
每单位时间发生某事件 $\lambda$ 次,则 $Exp(λ)$ 代表每次发生的时间间隔的概率分布。
泊松分布 / Poisson distribution
$$ Poisson(λ) $$
随机事件发生次数的数学期望值和方差均为 $\lambda$,则 $Poisson(λ)$ 为单位时间内随机事件发生的次数的概率分布。
服从泊松分布的随机变量,其数学期望与方差相等,均为 $\lambda$。
取样样本数很大时将近似正态分布。
伽玛分布 / Gamma distribution
$$ Gamma(a, \lambda) $$
发生 a 次独立的随机事件,每单位时间发生某事件 $\lambda$ 次,则 $Gamma(a, \lambda)$ 代表这 a 次事件发生总共所用时间的分布。
a 为 1 时,退化为指数分布。
几何分布 / Geometric distribution
$$ G(p) $$
即不停做实验直到成功为止,做实验的次数的概率分布。
负二项分布 / Negative binomial distribution
$$ NB(r, p) $$
即不停做实验直到第 r 次成功为止,做实验的次数的概率分布。
r 为 1 时,退化为几何分布。
负二项分布可以看作是 Gamma 分布和 Poisson 分布的组合。
$$ GammaPoisson(\lambda, \Phi) $$
其中:
$$ r = \frac \lambda \Phi $$
$$ p = \frac 1 {1 + \Phi} $$
正态分布 / Normal distribution
$$ N(\mu, \sigma^2) $$
假设一个实验可能有几种等可能的不同的结果,以多个(越多越好)这样的实验为一组,大量做这样的实验,每组实验的结果之和服从正态分布。
$\beta$-binomial 分布
$$ BetaBinomial(N, a, b) $$
是 Beta 和 Binomial 组合的结果,当 $p$ 服从 $Beta(a, b)$ 时,$Binomial(N, p)$ 的分布。
即每次试验得到“成功”结果的概率符合 $Beta(a, b)$,做 $N$ 次试验,得到“成功”次数的概率分布。
Bayes’ theorem
$$ 后验概率 = normalize(似然函数 \times 先验概率) $$
或者用符号写:
$$ Pr(p|W) = \frac {Pr(W|p)Pr(p)} {Pr(W)} $$
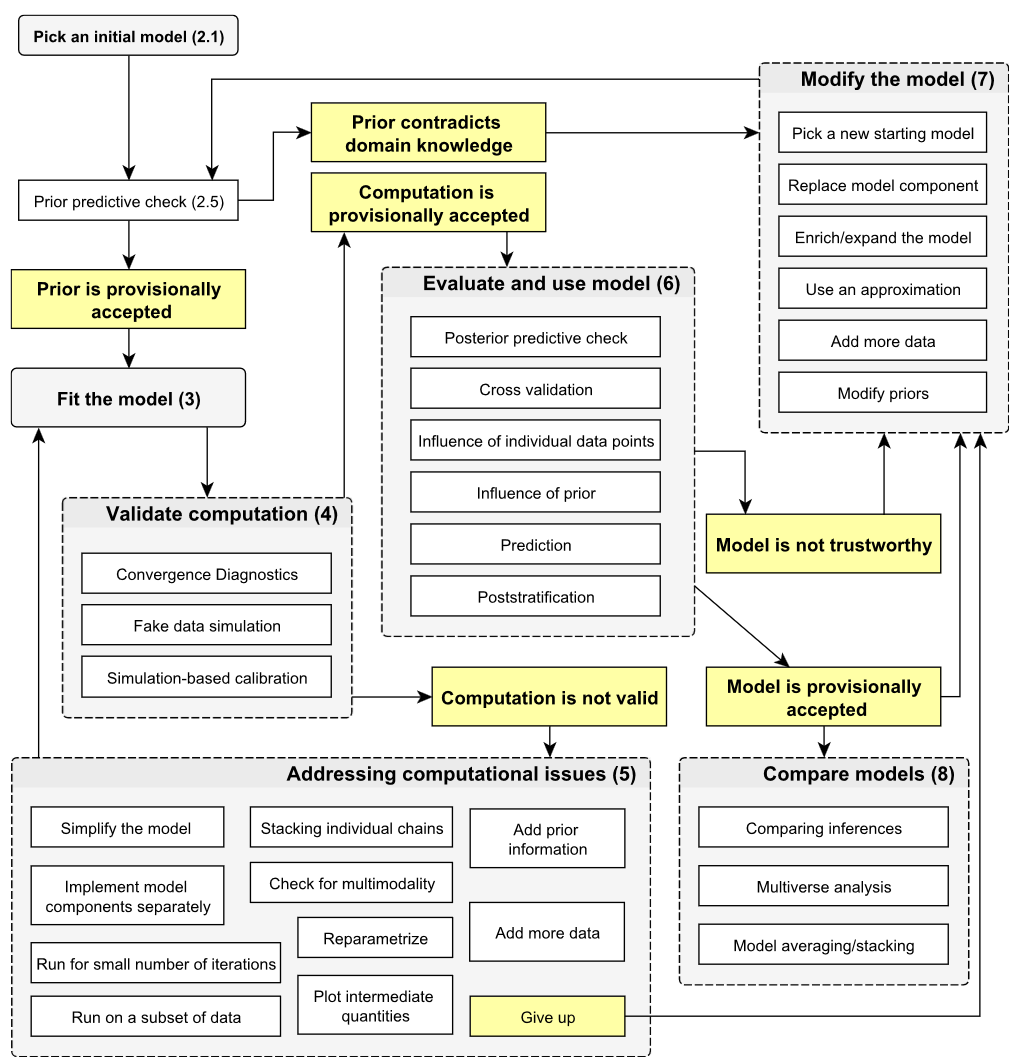
贝叶斯数据分析的步骤
本文严格区分事件(写作 $E_{大写英文字母}$)和变量(用普通大写英文字母表示),例如 $E_A$ 可能代表事件 $X=1$,同时可以给他分配变量 $A$,因此 $Pr(E_A) \equiv Pr\{X=1\} \equiv Pr(A)$。
$,$ 的优先级高于 $|$,例如 $Pr(p|W,L)$ 是 $Pr(p|(W,L))$。
$Y \mathrel{\rlap{\perp}\mkern1mu\perp} X | Z$ 的意义是:除去 $Z$ 的影响后(显示出) $Y$ 与 $X$ 无关,这是一个 conditional independency 的例子。
成功率并不一定是 $\frac a {(a+b)}$!$\frac a {(a+b)}$ 只是得到的分布中密度最大的点!
